As a business owner, you’ve likely encountered terms like CPM, CPC, and PPC in conversations with marketers and advertising agencies. Yes, there are important metrics for analyzing, tracking, and optimizing digital advertising effectiveness, as well as the billing methods for digital ads. In this article, Optimal Marketing Agency will guide you through understanding these commonly used terms. This will help you gain a solid grasp of marketers and agencies reporting content, enabling you to develop your own performance analysis strategies.
The effectiveness evaluation methods for digital advertising
For traditional print or digital media, advertising pricing is often based on factors such as the size, location, and timing of magazine or website placements. However, it’s not always possible for media outlets and advertisers to determine how many people actually saw these ads or how much they influenced behavior.
Digital advertising platforms like Facebook (FB), Instagram (IG), and Google have a distinct advantage in that they can provide clear metrics on ad exposure, click-through rates, views, viewing time, and likes, among other user behaviors. This allows you to calculate how much user behavior change your ad spending brings about, thus assessing the cost-effectiveness of your advertising.
You can think of Facebook or other digital advertising platforms as your customer acquisition assistants. These assistants deliver your ads to users who meet your specified criteria, and you can use the following indicators to evaluate their performance.
What is CPM?
CPM (cost per mile, or cost per thousand impressions) represents the cost per thousand times ad appears on users’ screens. In other words, it’s the expense for Facebook’s customer acquisition assistants to show your ad to users 1000 times. A lower CPM indicates better cost-effectiveness for ad exposure. The calculation formula is as follows:
- CPM = Total Ad cost/ ad impression x 1000
If you see CPM = 5 in the Meta ads manager, it means that Facebook charges you $5 for every 1000 ad impressions.

What is a good CPM?
After obtaining the CPM (Cost Per Mille), you can evaluate whether this advertising CPM is good or not using the following three comparison methods:
- Comparison with Platform Averages: Compare your CPM to the average data of the advertising platform. For example, according to data from the U.S. digital marketing company, the overall average CPM for Facebook in 2024 is $7.19. If your Facebook ad audience is in the Taiwanese market, your CPM should be lower than this figure.
- Comparison with Other Advertising Methods: If you are simultaneously purchasing digital ads on different platforms, such as Facebook ads and TikTok ads, comparing CPM can help you understand which advertising platform offers better exposure cost-effectiveness.
- Comparison with Your Own Other Ads: If you have multiple ad sets and creative variations on the same advertising platform, you can assess which combination of ad materials, messaging, and audience performs better. Optimize by emphasizing high-performing ads and adjusting or discontinuing underperforming ones to continually improve the cost-effectiveness of your ad campaigns.
In 2023, you can refer to the table below for CPM data from major advertising platforms. It’s important to note that the significance of CPM for Google keyword ads and shopping ads is limited. These types of ads are typically focused on click-through rates (CTR). When your keyword ads have a very high CTR (indicating strong audience appeal), the CPM may naturally be higher because your ad hasn’t been seen by many people yet. However, this is actually a positive sign, as it means your budget is being spent on clicks.
| Advertising Platforms | Facebook ads | Instagram ads | Google Keyword Ads | Google Shopping Ads | Google Display Ads |
| Industry Average CPM | US$7.19 | US$10.31 | Not specified | Not specified | US$3.12 |
The reason CPM (Cost Per Mille) is meaningful for platforms like Facebook (FB), Instagram (IG), and Google Display is because when users see these ads, their intentions aren’t always clear. As a result, the click-through rate (CTR) tends to be lower compared to keyword-based ads. Additionally, video ads, which unavoidably play in front of users, contribute to brand awareness. If you want to reduce your CPM, feel free to contact Optimal Marketing Agency.
What is CPC (cost per click)?
It’s the cost you pay for each individual click on your ads. In simple terms, when someone clicks your ad, you incur a cost. Imagine it like this: the friendly Facebook ad messenger shows your ad to users, and if some of them express interest by saying, “I want to learn more,” the messenger provides additional information. A lower CPC means that the digital advertising platform has secured a lower cost for each user click on your ad, resulting in better cost-effectiveness for your ad clicks.
- CPC = Total Ad Cost / Number of Ad Clicks
For example, if you see CPC = 10 in the Meta Ad Manager, it means that every time someone clicks your ad, Facebook charges you $10.
What is a good CPC?
In 2023, you can refer to table for CPC data from major advertising platforms. Keep in mind that this date is from Wordstream, a U.S. digital marketing company, so U.S. ad costs tend to be higher than in Taiwan. If you’re targeting the Taiwanese market on these digital platforms, your CPC should ideally be lower than the figures listed:
| Advertising Platforms | Facebook Ads | Instagram Ads | Google Keyword Ads | Google Shopping Ads | Google Display Ads |
| Average CPC across all industries | $0.83 | $0.5-$0.75 | $3-$4.22 | $0.66 | $0.63 |
What is CTR?
The term “CTR” stands for click-through rate. It represents the percentage of users who click on your ad after seeing it. Let’s break it down:
Imagine your Facebook ad is shown to users 100 times.
Out of those 100 views, a few users find it interesting and click on it.
The CTR is calculated as follows:
- CTR = Clicks / Impressions x 100%
For example, if your ad appears 100 times and 5 people click on it, your CTR would be 5% (5/100 * 100%).
What is a good CTR?
A higher CTR indicates that your audience is more interested in your ad, while a lower CTR suggests less interest. Digital advertising platforms prefer ads with higher CTRs because they provide a better user experience. If your CTR is too low, the platform may increase your ad costs.
Now, what’s considered a good CTR? Here are approximate ranges based on data from Smart Insights and Store Grower:
| Advertising Platforms | Facebook Ads | Instagram Ads | Google Keywords Ads | Google Shopping Ads | Google Display Ads |
| Average CTR across all industries | 0.16% to 1.11% | 0.22% to 0.33% | 4.7% to 11.8% | 0.86% | 0.46% |
Remember that a high CTR doesn’t necessarily mean an ad is most effective. It varies across platforms, and context matters. For instance, Google keyword ads have a higher standard for CTR compared to other platforms.
What is CPV?
The term CPV stands for cost per view. It represents the cost incurred each time your ad video is viewed.
CPV is calculated as follows:
CPV = total advertising cost / number of video views
On the Facebook Ads platform, views can be customized in various ways. For example:
- Some views count when users watch the entire video.
- Others count when users watch a certain duration (e.g., 3 seconds or more).
- If you see a Thruplay cost of $7 in the Meta Ads Manager, it means that every time someone watches your ad video completely, Facebook charges you $7.
What is a good CPV?
Determining what’s considered a good CPV can be challenging because different platforms have varying criteria for charging based on video length. For instance:
- YouTube charges after users watch 30 seconds or more.
- Facebook may charge after just 3 seconds of viewing.
- To compare, you can look at average CPV across platforms or compare your ads within the same platform.
Here’s a rough range for CPV on different platforms:
| Advertising Platforms | Facebook Ads | YouTube |
| Billing method | Watch for 3 seconds or watch the whole thing and you will be charged | Billing for viewing more than 30 seconds |
| CPV range | $0.01-$0.15 | $0.026 |
What is CPA?
CPA stands for cost per action/acquisition. It represents the cost incurred for each desired action taken by users on your website. These actions could include adding items to the cart, creating wishlists, making purchases, or other interactions.
The formula for calculating CPA is as follows:
- CPA = total advertising cost / number of results
For example, let’s say you tell Facebook Ads that your goal is to drive customers to make purchases in your store. If your ad budget is $10,000 and it results in 5 orders, your CPA would be:
- CPA=10000/5=2000
Keep in mind that “conversions” don’t have to be limited to orders. On Facebook, you can track various types of conversions. For instance:
- If your goal is to have users fill out inquiry forms on your website, you can calculate the cost per lead (CPL) using the same principle.
Setting a CPA limit
Suppose your objective is to drive purchases on your e-commerce website. Facebook will automatically optimize to bring as many purchase actions as possible. However, this might lead to a higher CPA than expected, affecting your ad costs and profitability. Imagine if your product price is $100, with a gross profit of $30, but each conversion costs $30 – that wouldn’t be ideal.
To avoid this situation, you can set a target CPA within Facebook to ensure it doesn’t exceed your desired value. This way, you maintain control over your costs while achieving your business goals.
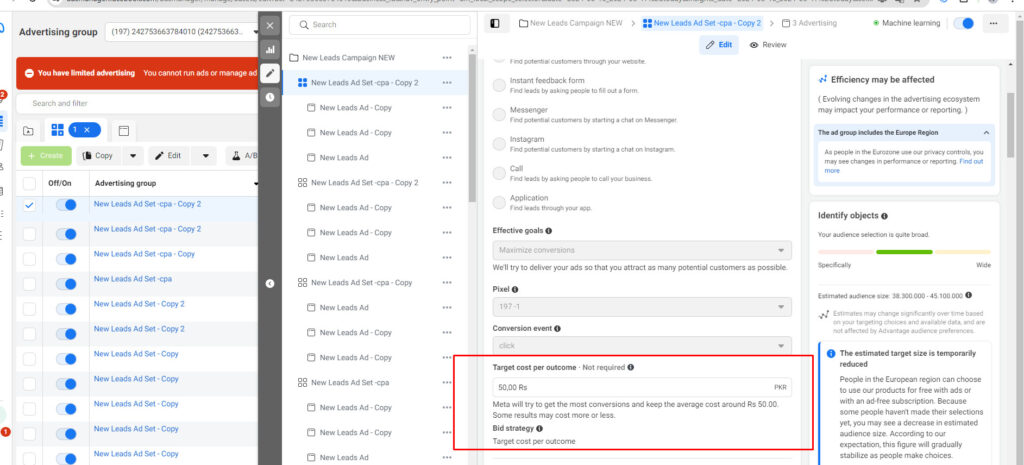
Imagine that a customer solicitation guy on Facebook is facing a huge crowd of users to recruit customers. Some customers are rich and particularly popular. There are many advertisements inviting them to visit your store. So it will cost Facebook a lot to attract them to your store. Time, Facebook guy’s service fee will be higher. When you set the cost per result, you are telling the Facebook guy to bring customers to my store, but if the customer is too valuable, don’t use it yet.
What is good CPA?
“CPA” has countless variations, and if you calculate carefully, each one is actually slightly different. Due to the varying metrics used in different industries, the differences can be significant. For e-commerce, the primary goal is usually sales. Below is a reference table for average e-commerce CPAs across different advertising platforms:
| Advertising Platform | Facebook Ads | Google Keyword ads | Google shopping ads | Google Display ads |
| CPA | Overall industry average: US$18.86 | E-commerce average: US$45.27 | E-commerce average: US$38.87 | E-commerce average: US$65.80 |
| Apparel: US$10.98 | Beauty: US$25.49 | Retail: US$21.47 |
Keep in mind that these figures are averages and can vary based on specific circumstances and strategies.
What is CVR?
CVR (Conversion Rate) is similar in concept to the previously mentioned CTR (Click-Through Rate). It refers to the percentage of users who take the desired action out of those who clicked on an ad. The term “conversion” in this context relates to the desired outcome (such as adding items to a cart, creating a wishlist, filling out a form, or making a purchase). These actions bring users closer to your goal and can be set as conversions within Facebook (FB) for calculation.
The formula for conversion rate is as follows:
- Conversion Rate=Impressions/Conversions×100%
To illustrate, suppose your goal with Facebook ads is sales. If the FB ad reaches 100 users, and 5 of them not only visit your store but also make actual purchases, the conversion rate would be 5%.
You can customize your conversion rate metric based on your specific needs. Use different numbers as the denominator (impressions, clicks, or reach) and select the most relevant user actions as the numerator (e.g., form submissions, purchases, Facebook messages). By configuring the desired formula in the Facebook Ads Manager, you can directly track the conversion rates for each ad.
For example, if today you want to know how many people out of all those who saw your ad eventually placed an order on your website, you can create a custom metric: “Number of Purchases / Reach.” By doing this, you’ll be able to see the conversion rate for each ad in the FB Ads Manager.
What is good CVR?
Every business owner and every advertisement have different conversion goals, so it’s not always possible to find a reference standard. Different digital advertising platforms also have varying strengths in terms of conversions. However, you can compare your conversion rates for the same goal but different ad campaigns on the same advertising platform, as well as compare your advertising results across different platforms. Here are the conversion rates for different platforms:
| Advertising platforms | Facebook Ads | Instagram Ads | Google keyword ads | Google shopping ads | Google display ads |
Apparel: 4.11%, Beauty: 7.1%, Retail: 3.26% | 1% | E-commerce conversion rate: 2.8% | E-commerce conversion rate: 1.91% | E-commerce conversion rate: 0.59% |
How digital advertising is billed
Frequently, alongside CPM and CPC, you might hear about PPC, PPM, and PPA. These three terms refer to different billing methods in digital advertising:
- PPM (Pay Per Mille/Thousand Impression): This method charges based on every thousand impressions. The cost to acquire each thousand impressions is equivalent to CPM.
- PPC (Pay Per Click): With PPC, advertisers pay for each click. The cost to acquire each click is represented by CPC.
- PPA (Pay Per Action): PPA involves paying based on specific actions or conversions. The cost to acquire each action (such as a sale or lead) is denoted by CPA.
Now, let’s discuss how to reduce advertising costs and improve conversion rates:
- Focus on Ad Quality: Invest effort into creating engaging ads. Ideally, your ad should be so enjoyable that users can’t resist liking and sharing it. While achieving zero ad cost is challenging, improving ad quality can help.
- Audience Expansion: Avoid targeting too narrow an audience. When the audience is too small, both CPM and CPC tend to increase due to heightened competition.
- Avoid Ad Overlap: Don’t simultaneously serve different ads to the same audience. Overlapping ads can lead to increased competition and higher costs.
- Refine Ad Messaging: Ensure that your ad message resonates with the audience. If users find the ad irrelevant, platforms like Facebook may penalize it, resulting in higher CPM and CPC.
- Incentivize Clicks: Leverage influencers or Key Opinion Leaders (KOLs) to encourage clicks. Include promotional messages in your ads.
- Experiment with Ad Formats: Try different ad formats. For instance, Facebook carousel ads tend to have higher click-through rates than other formats.
- Frequency Control: Avoid bombarding the same disinterested audience with repetitive ads. High frequency can inflate ad costs.
- Lookalike Audiences: Use Facebook’s lookalike audiences based on past buyers. Let Facebook find similar audiences to those who have already made a purchase.
- A/B Testing: Conduct A/B tests to identify methods that lead to lower ad costs.
- Seek Professional Assistance: Consider hiring digital advertising experts to manage your campaigns effectively.
In conclusion
Optimal Marketing Agency helps you reduce advertising costs and increase conversion rates
In this article, Optimal marketing agency shares definitions, calculation methods, and usage of six important digital advertising effectiveness indicators: CPM, CPC, and CPV. The goal is to help business owners better evaluate advertising performance. Whether an ad campaign is profitable depends on factors like product, market, and advertising strategy. Optimal marketing agency specializes in using digital advertising to reach the right audience and leverages accumulated data and experience to minimize ad costs. By doing so, business owners can focus on creating customer value and competitive advantages. Let’s work together to find the formula for success!
